Japanese mustard Mizuna BIO
Japanese mustard Mizuna BIO
Couldn't load pickup availability
Japanese mustard Mizuna
Growing Japanese mustard, Mizuna, is a straightforward process. Here’s a guide to help you cultivate Mizuna successfully:
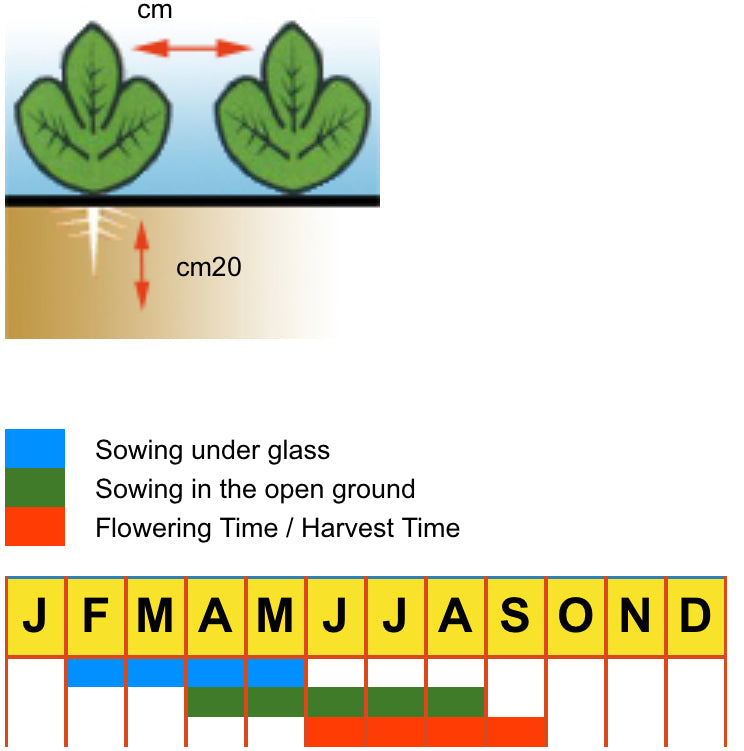
1. Planting Time: Mizuna is a cool-season crop. Plant seeds directly in the garden in early spring or late summer for a fall harvest.
2. Site Selection: Choose a location with partial shade to full sun. Mizuna prefers cooler temperatures, making it suitable for spring and fall plantings.
3. Soil Preparation: Ensure the soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter. Work in compost or well-rotted manure to improve soil fertility. Mizuna prefers slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0.
4. Planting Seeds: Sow Mizuna seeds directly into the soil about 1/4 inch deep. Space the seeds according to the recommended spacing on the seed packet.
5. Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during dry periods. Water Mizuna regularly to prevent the soil from drying out. Adequate moisture is crucial for tender leaves.
6. Thinning: Thin the Mizuna seedlings once they are a few inches tall to ensure proper spacing. This promotes good air circulation and allows the plants to develop well.
7. Fertilization: Mizuna is not a heavy feeder, but you can apply a balanced fertilizer at planting time. Side-dress with additional fertilizer during the growing season if needed.
8. Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch around the Mizuna plants to retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
9. Harvesting: Harvest Mizuna leaves when they are young and tender, usually around 4-8 inches tall. You can harvest individual leaves or cut the entire plant about 2 inches above the soil to encourage regrowth.
10. Successive Planting: For a continuous harvest, consider successive plantings every few weeks. This ensures a fresh supply of Mizuna throughout the growing season.
11. Pest and Disease Control: Keep an eye out for common pests such as aphids or flea beetles. Insecticidal soap or neem oil can be used for organic pest control. Practice good garden hygiene to minimize disease issues.
12. Storage: Use harvested Mizuna promptly for the best flavor and texture. If you have excess, you can store it in the refrigerator for a short period.
Growing Mizuna adds a mild and peppery flavor to salads and other dishes. Enjoy cultivating this versatile Japanese mustard in your garden!
Share